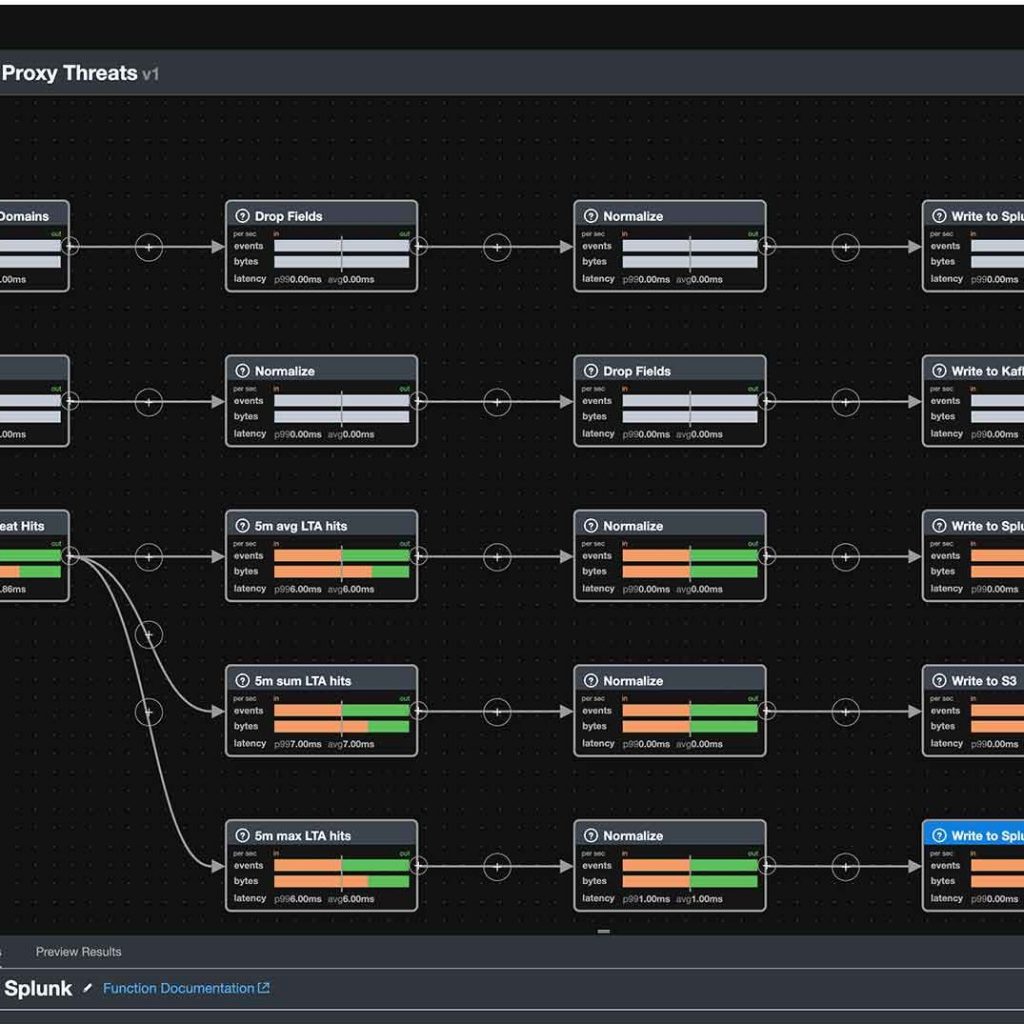
What is the Splunk Data Stream Processor?
The Splunk Data Stream Processor (DSP) is a data stream processing service that manipulates data in real time and shoots that data over to your preferred platform. Splunk DSP provides the ability to continuously collect high-velocity, high-volume data from diverse data sources, and distribute it to multiple destinations in milliseconds.
Stream processing is the processing of data in motion, it is designed to analyze and compute data instantaneously as it is received. The majority of data sources are born in continuous streams, so being able to process them as such provides almost real-time insight into events for your analysts.
Batch Processing vs. Data Stream Processing
This is different from the “standard” data processing called batch processing. Batch processing collects the data (in batches) and then processes that data. The benefit to Stream processing is that you will have immediate insight into your critical events and can act on notable events more quickly.
How to Use Splunk Data Stream Processing (+Examples)
Use Case #1: Data Filtering/Noise Removal
With DSP, you can filter or route non-useful and noisy logs to a destination of your choice. This use case allows you to route these logs to a separate syslog or storage solution for aggregation, but it is outside of Splunk, so it does not affect your Splunk license and it doesn’t fill your indexes with unwanted data.
Use Case #2: Data Routing
With DSP, you can receive a high-velocity and high-volume of data to multiple destinations. This use case allows you to send your data to Splunk, containers, S3, syslog aggregate, and more at a rapid pace. This allows you to split the data to send to multiple destinations at the source without first indexing the data into Splunk and then sending it off. This allows for more efficient data flow.
Use Case #3: Data Formatting
With DSP, you can format your data using provided functions based on your configured conditions. This is a fairly straightforward use case allowing you to format your events to make your raw logs human-readable and informative without having to first index the data into Splunk. This can be combined with any of the use cases in this list to achieve maximum value with DSP.
Use Case #4: Data Aggregation
With DSP, you can aggregate data based on configured conditions and identify abnormal patterns in your data. You can pre-configure rules or conditions that will send data to different aggregate points based on the patterns within the data, that pertain to the rules configured. If you have a data source with a mixture of different kinds of logs, you can now pick up all the logs and forward them to different destinations with ease.
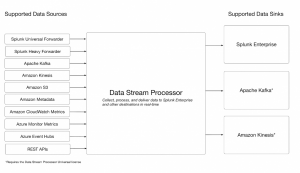
Data Sources for Data Stream Processing
First, look into what data sources are supported by Splunk DSP. Here are the data sources that are currently supported by the current version. Be on the lookout for more data sources that to be added in future releases.
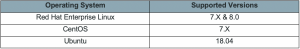
Here are the system requirements that come with Splunk DSP.
The Advantages and Disadvantages to Splunk’s Data Stream Processor
Although this tool is powerful and has a ton of use cases (which we discuss below), take a minute to understand the benefits and drawbacks before you dive head-first into it.
Pros of Splunk Data Stream Processor
- Real-time data processing: The Data Stream Processor can process data in real time and allow users to get insights on data as it’s being generated.
- Support for several data sources and formats: It can ingest data from a wide range of sources, including IoT devices, sensors, social media, and even machine-generated data.
- Flexible deployment options: The tool can be deployed in a variety of environments, including on-premises, in the cloud, and in hybrid environments.
Cons of Splunk Data Stream Processor:
- Cost: Splunk DSP can be expensive, especially for organizations with large data volumes.
- Steep learning curve: There’s a pretty steep learning curve with DSP and will require some level of Splunk expertise to use it.
- Resource-intensive: It requires significant CPU and memory resources to operate.
We’ve been more than excited about the release of this data stream processing service and we hope you are too. If you’re interested in learning more about Splunk Data Stream Processing, we’re here to help. You don’t have to master Splunk by yourself in order to get the most value out of it. Small, day-to-day optimizations of your environment can make all the difference in how you understand and use the data in your Splunk environment to manage all the work on your plate.
Cue Atlas Assessment: a customized report to show you where your Splunk environment is excelling and opportunities for improvement. Once you download the app, you’ll get your report in just 30 minutes.